Kevin T. Chen1, Olalekan Adeyeri2, Tyler N Toueg3, Elizabeth Mormino3, Mehdi Khalighi1, and Greg Zaharchuk1
1Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Salem State University, Salem, MA, United States, 3Neurology and Neurological Sciences, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
1Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Salem State University, Salem, MA, United States, 3Neurology and Neurological Sciences, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
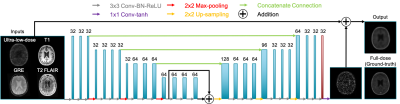
We aimed to investigate whether a pre-trained ultra-low-dose amyloid PET/MRI network could generalize to ultra-low-dose tau PET image enhancement. Results showed that data bias needs to be accounted for before applying an ultra-low-dose network trained on one tracer to another.
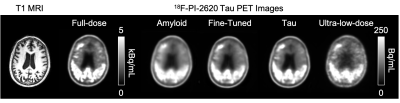
Figure 2. Representative tau PET images and their corresponding T1-weighted MR image in a patient with significant cortical uptake. The synthesized PET images show greatly reduced noise compared to the low-dose PET image, while the images generated from the Tau Network and the Fine-tuned Network were superior in reflecting the underlying anatomical patterns of the tau tracer uptake. The image obtained directly from the Amyloid Network performed less well, with more image blurring.