Emre Kopanoglu1
1CUBRIC, School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom
1CUBRIC, School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom
Pulses designed using patient-specific B1+-maps
are inherently patient position dependent, while safety models used for local
SAR supervision are not. The actual local SAR at off-centre positions was observed
to be up to 4.6-fold higher compared to the peak estimated using a centred
model.
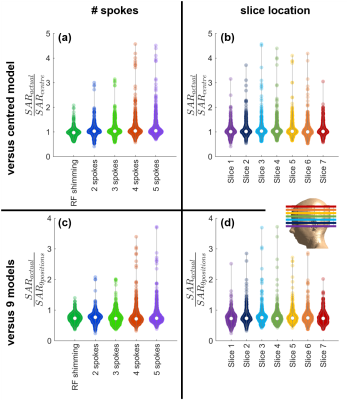
Figure 2: psSAR-actual is compared with (a-b) psSAR-centre
and (c-d) psSAR-9positions. (a-b) The actual peak local SAR was up to 4.6-fold higher
than the peak estimated using the centred safety model. The sensitivity of psSAR
to positional mismatch increased with the number of spokes but remained fairly
consistent across slices (15/21 comparisons between slices yielded p>0.05).
(c-d) Using 9 body models reduced the sensitivity of psSAR to positional
mismatches. Nevertheless, the actual SAR was still up to 3.7-fold higher than
the peak estimated using the 9 models.
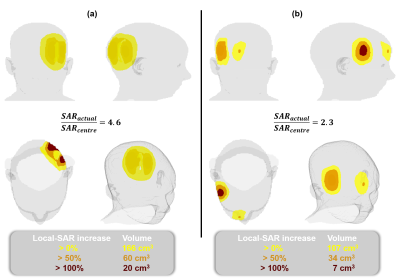
Figure 4: The regions that were exposed to higher levels of
local SAR than the estimated maximum due to the positional mismatch are shown
for two selected positions. (a) A region of size 166 cm3 was exposed
to elevated levels of local SAR at the worst-case scenario. 20 cm3 of tissue was exposed to more than twice the estimated maximum local SAR. (b) The positional
mismatch caused elevated levels of SAR exposure in the right anterior part of
the head in a different case.
