Gaurav Verma1, Paul Min2, MyungHo In2, Jungho Cha3, Akbar Alipour1, Charlotte Elorette4, Lazar Fleysher5, Priti Balchandani1, Helen Mayberg3, and Ki Sueng Choi3
1Radiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 2Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States, 3Center for Advanced Circuit Therapeutics, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 4Neuroscience, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 5Diagnostic, Molecular and Interventional Radiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States
1Radiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 2Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States, 3Center for Advanced Circuit Therapeutics, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 4Neuroscience, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 5Diagnostic, Molecular and Interventional Radiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States
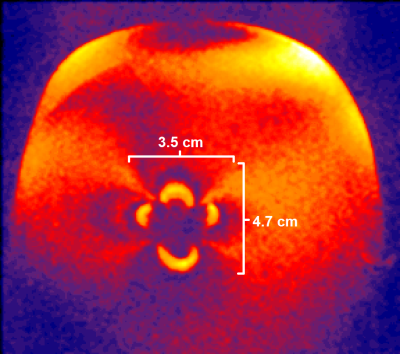
Radio frequency (RF) safety and image quality testing was performed in the presence of deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrodes using gel acrylamide phantoms and two 3T MRI scanners. Both tests showed improved performance when electrodes were aligned along B0 field and normal to transmit field.