Mohaddese Mohammadi1, Elena Kayee1, Youngwook Kee1, Jennifer Golia Pernicka 2, Iva Petkovska2, and Ricardo Otazo 2
1Medical physics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
1Medical physics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
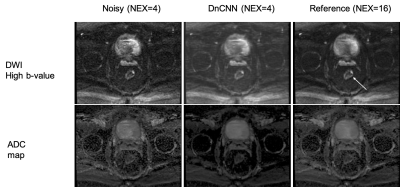
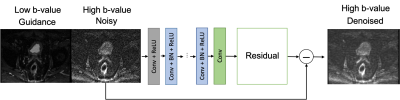
Both the denoised high b-value image and resulting denoised ADC map compare favorably to the original noisy results and approximate the results obtained with the reference image. This result indicates that accelerating rectal DWI by reducing the number of acquired averages is feasible.