Endre Grøvik1,2, Darvin Yi3, Franziska Knuth4, Sebastian Meltzer5, Anne Negård5, and Kathrine Røe Redalen4
1Department for Diagnostic Physics, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway, 2Faculty of Health Sciences, University of South-Eastern Norway, Drammen, Norway, 3University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States, 4Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 5Akershus University Hospital, Lørenskog, Norway
1Department for Diagnostic Physics, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway, 2Faculty of Health Sciences, University of South-Eastern Norway, Drammen, Norway, 3University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States, 4Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 5Akershus University Hospital, Lørenskog, Norway
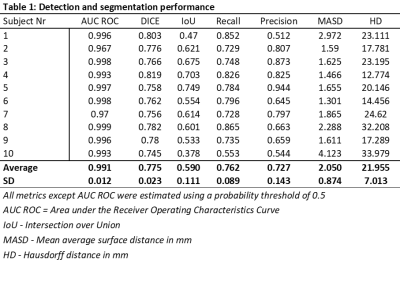
Our deep learning model demonstrates high performance in detecting and segmenting rectal cancers, equivalent to that of an expert reader. This work show the potential use of deep learning-based segmentation in a clinically relevant setting.
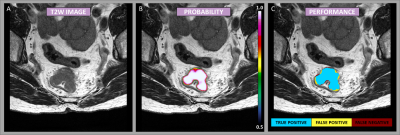
Figure
1: Example case showing the segmentation performance from the DeepLab V3
network. The image mosaic shows the T2-weighted image-series [A], the
predictions as probability maps [B] (voxel-wise ranging from 0.5 to 1 as
indicated by the color bar), and performance maps [C] classified as true
negative, false positive, and false negative as specified by the color code.