Toshiaki Taoka1,2, Rintaro Ito1,2, Rei Nakamichi2, Takashi Abe2, Toshiki Nakane2, Hisashi Kawai2, Mayuko Sakai3, and Shinji Naganawa2
1Department of Innovative Biomedical Visualization (iBMV), Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 2Radiology, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 3Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan
1Department of Innovative Biomedical Visualization (iBMV), Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 2Radiology, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 3Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan
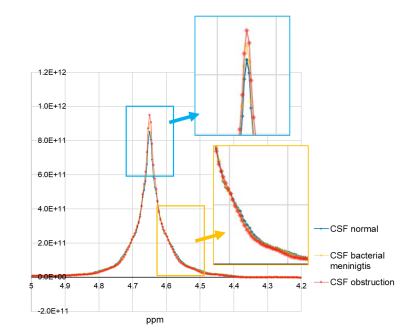
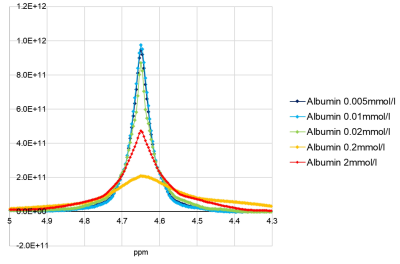
Water peaks in MRS changed with the solute
concentrations of NaCl, Glu, and Alb. Differences in water peaks were observed
among the CSF phantom simulating normal, bacterial meningitis, and obstruction
of the subarachnoid space samples.