Gerhard Drenthen1, Jacobus Jansen1, Paulien Voorter1, Joost de Jong1, and Walter Backes1
1Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht, Netherlands
1Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht, Netherlands
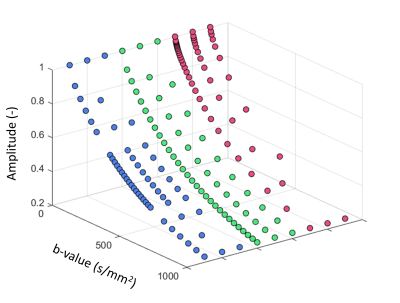
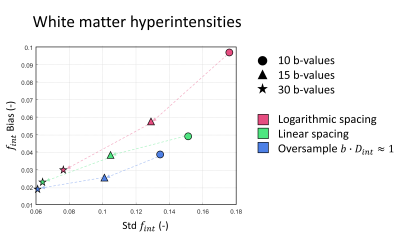
When a large intermediate diffusion component is present in the IVIM signal (eg. white matter hyperintensities), b-value sampling strategies specifically aimed to quantify this component can provide better estimates of $$$f_{int}$$$ compared to linear or logarithmic spaced b-values.