Rutwik Shah1, Bruno Astuto Arouche Nunes1, Tyler Gleason1, Justin Banaga1, Kevin Sweetwood1, Allen Ye1, Will Fletcher1, Rina Patel1, Kevin McGill1, Thomas Link1, Valentina Pedoia1, Sharmila Majumdar1, and Jason Crane1
1Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States
1Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States
Swarm predictions for both cohorts (radiologists and residents) were
closer to clinical ground truth, outperformed their own individually graded
labels and the AI predictions. Accuracy of resident performance also
improved with increase in swarm size (three versus five participants).
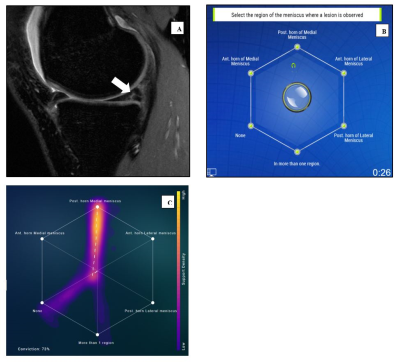
Figure 1: A) Sagittal cube sequences evaluated for meniscal lesions (arrow
pointing to post. horn tear in medial meniscus). B) Swarm platform interface
used to derive consensus grades for location of lesion. C) Visualization of the
trajectory of decision made by the swarm. While there were individually
divergent opinions, the eventual consensus of the group in this example was for
posterior horn of the medial meniscus.
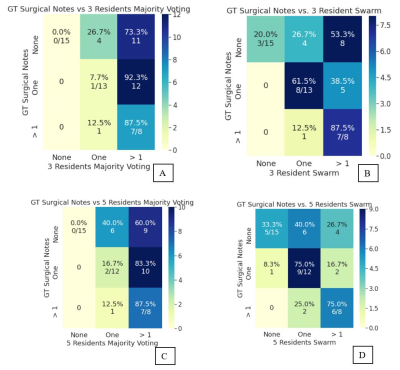
Figure 2: Resident
versus Ground truth (GT). A) Confusion matrix (CM) for 3 resident majority vote
vs GT (kappa: 0.01) B) CM for 3 resident swarm vs GT. Accuracy improves
compared to majority vote (kappa: 0.24) C) CM for 5 resident majority vote vs
GT (kappa: 0.05) D) CM for 5 resident swarm vs GT. Accuracy improves compared to
majority vote (kappa: 0.37).
Note: 5 resident swarm was unable to obtain a consensus on 1
exam, which was excluded during CM tabulation.
