Suheyla Cetin-Karayumak1, Evdokiya Knyazhanskaya2, Brynn Vessey2, Sylvain Bouix1, Benjamin Wade3, David Tate4, Paul Sherman5, and Yogesh Rathi1
1Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 2Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 4University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States, 5U.S. Air Force School of Aerospace Medicine, San Antonio, TX, United States
1Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 2Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 4University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States, 5U.S. Air Force School of Aerospace Medicine, San Antonio, TX, United States
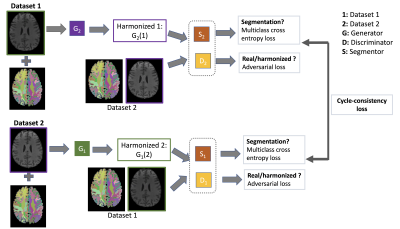
While the Dice overlap score was
91% between datasets from two scanners prior to harmonization, the Dice score
increased to 98% after harmonization in subcortical regions. This result proves
the efficacy of our multi-site T1 data harmonization approach.
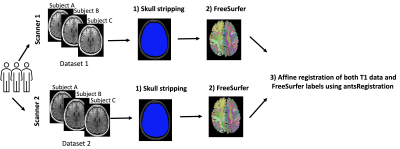
Figure 1. T1 data of 25 subjects were scanned using two
scanners. We refer to the T1 data from scanner 1 as dataset 1 and from scanner
2 as dataset 2. The data preprocessing steps included: 1) N4 bias field
correction and skull-stripping using our in-house software (https://github.com/pnlbwh/luigi-pnlpipe); 2) Creating label maps using FreeSurfer
v. 7.1.0; 3) Affine registration using antsRegistration.