Brian McCrindle1,2, Nicholas Simard1,2, Ethan Samson2,3, Ethan Danielli 2,3, Thomas E. Doyle1,3,4, and Michael D. Noseworthy1,2,3
1Electrical and Computer Engineering, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2Imaging Research Center, St. Joseph's Healthcare, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 3School of Biomedical Engineering, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 4Vector Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada
1Electrical and Computer Engineering, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2Imaging Research Center, St. Joseph's Healthcare, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 3School of Biomedical Engineering, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 4Vector Institute, Toronto, ON, Canada
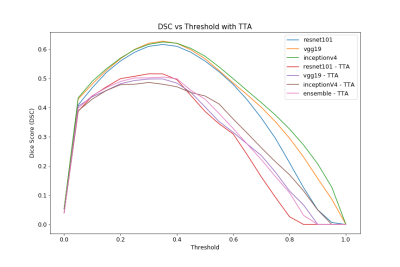
We develop a deep ensemble-based 2D-UNet framework for brain microstructural white matter damage segmentation. We show that ensembles perform the most reliably in out-of-distribution conditions even with minimal training data.
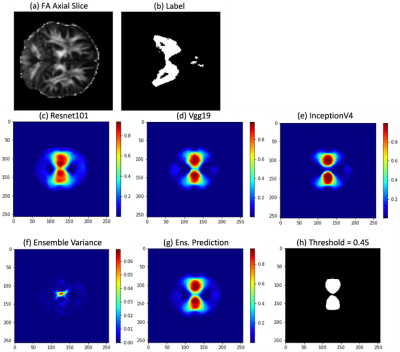
Example of an unseen slice fed into the ensemble model. (a) Normalized Axial FA Slice. (b) Z-Scoring label. (c – e) Model predictions for 2D-UNets with Resnet101, Vgg19, InceptionV4 Encoders with Dice scores 0.69, 0.69, 0.70 respectively. (f) Ensemble Predictive Uncertainty. (g) Ensemble Prediction. (h) Ensemble Prediction with “Optimal” Threshold and a Dice Score of 0.71.