Alistair Lamb1, Anna Barnes2, Stuart A Taylor2, and Hui Zhang3
1Department of Medical Phyics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Centre for Medical Imaging, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 3Centre for Medical Image Computing, University College London, London, United Kingdom
1Department of Medical Phyics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Centre for Medical Imaging, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 3Centre for Medical Image Computing, University College London, London, United Kingdom
A supervised deep-learning
approach to detect the presence of Nyquist ghosts in axial DWI slices of the abdomen
is proposed with intent for use in improving the reproducibility of
quantitative ADC measurements in the body. A test accuracy of 81.5% was achieved.
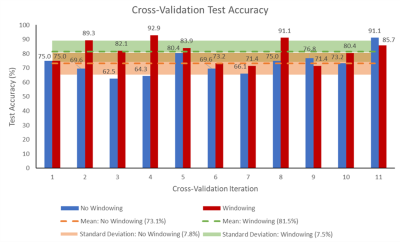
Figure 5: The percentage accuracy of the classifier on test
data for each of the 11 cross-validation iterations is shown, for both the
network trained on DWI slices with intensity values windowed between 0-25, and
for the network trained without windowing. The mean accuracy and corresponding
standard deviation across all 11 iterations is also shown for both cases.
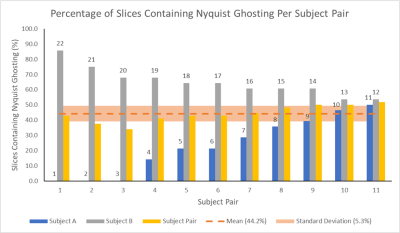
Figure 5: The
percentage of slices containing Nyquist ghosts is shown for each
pair of subjects. For each subject pair, the percentage for the constituent subjects are also shown, labelled
with the subject number. The mean (44.2%) across all subject pairs is given, along with the standard deviation (5.3%) which is much lower than that of slices containing Nyquist Ghosting in individual
subjects, as shown in Figure 2.
