Jiyoon Yoo1, Leevi Kerkelä1, Patrick W. Hales1, Kiran K. Seunarine1, Iulius Dragonu2, Enrico Kaden1, and Christopher A. Clark1
1UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, London, United Kingdom, 2Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Frimley, United Kingdom
1UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, London, United Kingdom, 2Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Frimley, United Kingdom
All-in-one sequence for microstructural imaging in the hippocampus, providing high-resolution images for localisation of hippocampal subregions and fitting of standard and advanced diffusion models.
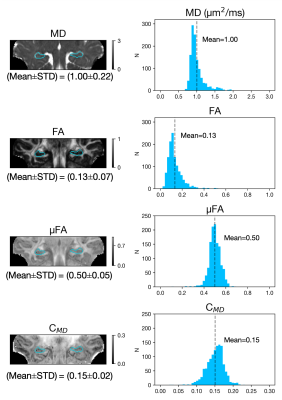
Figure 3. Derived microstructural maps and parameters. From top to bottom: Mean diffusivity (MD) from diffusion kurtosis fit, fractional anisotropy (FA) calculated from diffusion kurtosis fit, microscopic fractional anisotropy (μFA) from QTI, normalised size variance (CMD) from QTI. STD=standard deviation.
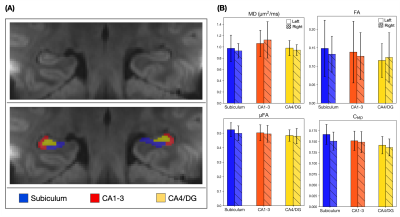
Figure 4. (A) Mean diffusion-weighted LTE image at b-value of 1000 s/mm2 shows contrast within the hippocampal subregions. Subregions were manually segmented for subiculum (blue), Cornu Ammonis (CA) regions CA1-3 (red) and CA4 with dentate gyrus (DG, yellow). (B) Microstructural parameters were calculated in each subregion; Subiculum, CA1-3 and CA4/DG.