Graham Little1 and Christian Beaulieu1
1Biomedical Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
1Biomedical Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
An
automatic surface-based deep grey matter segmentation method was developed that
works directly on brain diffusion images. As a demonstration, the method yielded
unique non-linear trajectories of diffusion metrics in deep grey matter regions
in healthy people aged 6-90 years.
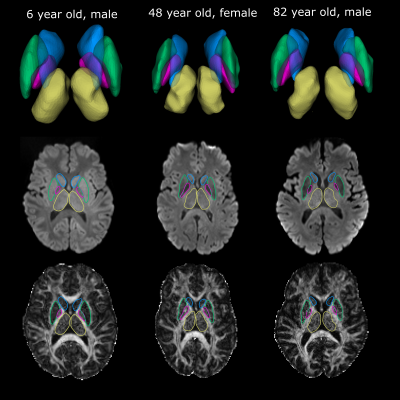
Figure 3. Deep grey matter
segmentations derived from workflow in Figure 2 displayed for three subjects
spanning a large age range. Segmentations
are displayed in 3D as well as on a single axial slice of the mean b1000
diffusion weighted image and FA map. Even
with substantial subject variability in brain shape, reasonably accurate
cortical segmentations were generated for each region
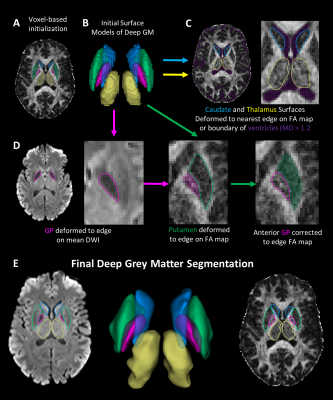
Figure 2. Segmentation workflow
of deep GM structure based solely on DTI. (A) Initial segmentations registered
from an atlas are (B) converted into surfaces.
(C) The caudate and thalamus are deformed to an edge on the FA map or
nearest ventricle edge (purple). (D) The globus pallidus (GP) is deformed on
the mean b1000 image. The putamen is deformed on the FA map preventing
deformation into the GP. A correction to the GP is applied on the FA map. (E) Visualization
of final deep GM segmentations.
