Henrik Lundell1, Samo Lasič1,2, Filip Szczepankiewicz3,4,5, Beata Wereszczyńska6, Matthew Budde7, Erica Dall'Armellina6, Nadira Yuldasheva6, Jürgen E. Schneider6, and Irvin Teh6
1Danish Research Centre for Magnetic Resonance, Centre for Functional and Diagnostic Imaging and Research, Copenhagen University Hospital Hvidovre, Hvidovre, Denmark, 2Random Walk Imaging, Lund, Sweden, 3Clinical Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 4Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 5Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 6Leeds Institute of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Medicine, University of Leeds, Leeds, United Kingdom, 7Department of Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States
1Danish Research Centre for Magnetic Resonance, Centre for Functional and Diagnostic Imaging and Research, Copenhagen University Hospital Hvidovre, Hvidovre, Denmark, 2Random Walk Imaging, Lund, Sweden, 3Clinical Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 4Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 5Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 6Leeds Institute of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Medicine, University of Leeds, Leeds, United Kingdom, 7Department of Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States
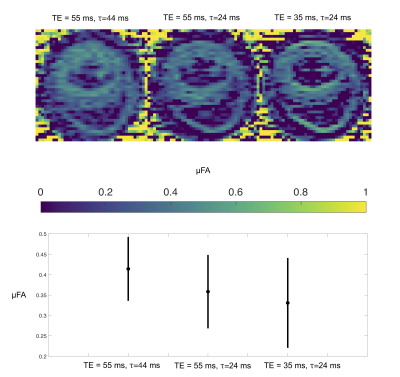
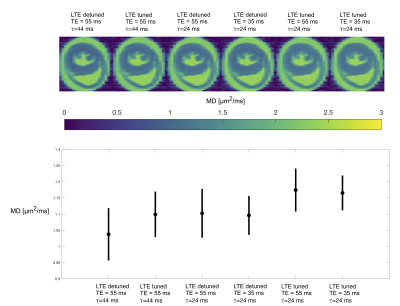
We suggest a battery of MDE measurements that probe diffusivity and microscopic anisotropy at different diffusion and echo times. We show a clear effect of time-dependent diffusion but a smaller effect from transversal relaxation.