Minghui Tang1, Kiyoi Okamoto2, and Toru Yamamoto1
1Faculty of Health Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan, 2Graduate School of Health Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
1Faculty of Health Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan, 2Graduate School of Health Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
The RF heating due to elbow-bore wall contact is dependent on the electric field distribution inside the MRI scanner, which is dominantly determined by the RF transmission coil.
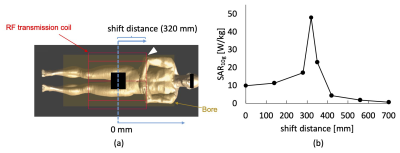
Fig. 1 (a) Simulated model (at 320-mm shifted distance) on the electromagnetic analysis software. The blue dashed line represents the center of the MRI scanner and the RF transmission coil. The blue arrows show the direction of human phantom shift. A white arrow head shows the contact point of the right elbow on the bore wall. (b) The SAR10g at the contact point versus the shift distance.
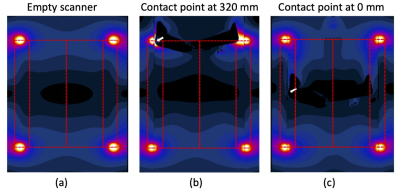
Fig. 2 The electric field distributions of (a) an empty scanner, (b) the position of contact point with 320-mm shifted distance, (c) the position of contact point at the center (0 mm). The white arrows show the contact points. The red dashed lines represent the projection of the birdcage transmission coil elements onto the plane of each map. To improve the visualization of the electric field strength near the human model, the color index was maximally scaled at 2000 V/m.