Soham Mukherjee1, Mahon L Maguire1, Jack Sharkey1, Sourav Bhaduri1, Patricia Murray2, Rachel Bearon3, Bettina Wilm2, and Harish Poptani1
1Centre for Preclinical Imaging, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom, 2Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom, 3Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom
1Centre for Preclinical Imaging, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom, 2Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom, 3Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom
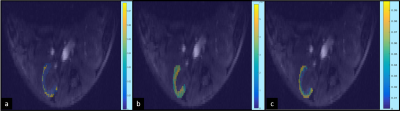
Dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance
imaging was used to determine the permeability parameter Ktrans, to
assess renal function.