Jing Yang 1, Shuohui Yang 2, Zheng He3, Mengxiao Liu4, and Caixia Fu5
1Nephrology, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China, 2Radiology, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China, 3Ultrasonography, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China, 4MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 5MR Applications Development, Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Shenzhen, China
1Nephrology, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China, 2Radiology, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China, 3Ultrasonography, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China, 4MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 5MR Applications Development, Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Shenzhen, China
BOLD-MRI and IDU evaluating
renal oxygenation and hemodynamics on CKD
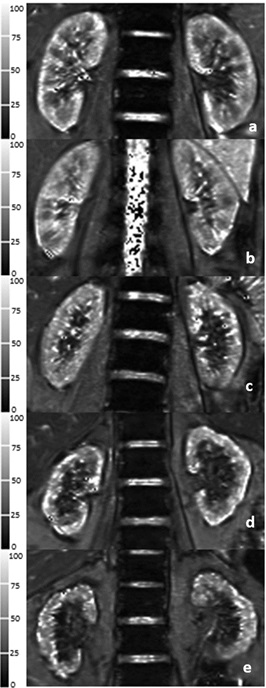
Fig.1 Five typical T2* images of BOLD-MRI in healthy
volunteer and CKD1-4 patients. a Healthy volunteer, male/26 years old. b
Stage 1 CKD patient, female/28 years old. c Stage 2 CKD patient, male/29
years old. d Stage 3 CKD patient, female/ 62 years old. e Stage 4
CKD patient, female/58 years old.
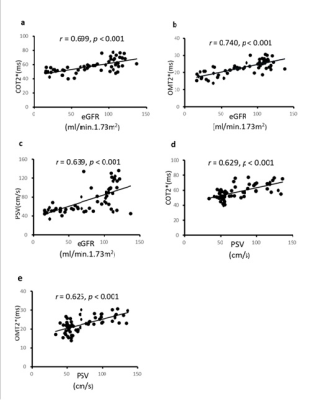
Fig.2 Correlation
coefficients among the cortical T2* (COT2*), outer
medullary T2* (OMT2*) values, peak systolic velocity (PSV), and
estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). a Correlation
of COT2* values and eGFR. b Correlation of OMT2*
values and eGFR. c Correlation of PSV values and eGFR. d Correlation
of COT2* values and PSV
values. e Correlation of OMT2* values and PSV. Spearman coefficient
testing was performed to assess statistical significance.