Limin Zhou1, Yiming Wang1, and Ananth Madhuranthakam1,2
1Department of Radiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States, 2Advanced Imaging Research Center, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States
1Department of Radiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States, 2Advanced Imaging Research Center, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States
In this study, we implemented and evaluated the optimized unbalanced
pCASL gradient scheme with perfusion
phantom and 4 healthy volunteers. The results showed this optimized
unbalanced pCASL gradient scheme was more robust to off-resonance than the
corresponding scheme of balanced pCASL.
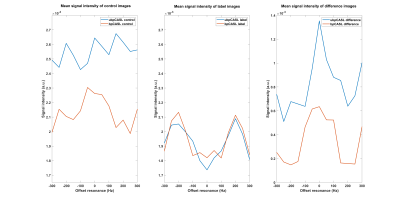
Figure 4. The
comparison of mean signal intensities in control (left), label (middle) and
difference (right) images of second subject’s kidney (fig.
3) between unbalanced pCASL (blue) and balanced pCASL (red) across different
off-resonance.
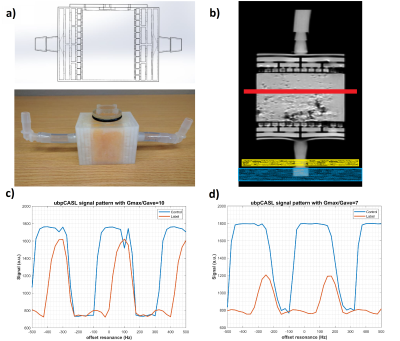
Figure 2. a) 3D
printed phantom mimics the branching vessels with input/output tubes connected
to the pump. b) Labeling plane (yellow) and inflow saturation setup (blue) for
2D image acquisition (red). c) and d) Control and label signal pattern among
different offset resonances of unbalanced pCASL (ubpCASL) with Gmax to Gave ratio of 10 and 7
respectively.
