Bowen Shi1, Ke Xue2, Yili Yin1, Qing Xu1, Binbin Shi1, Jing Ye1, and Yongming Dai2
1Northern Jiangsu Province Hospital, Yangzhou, China, 2Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
1Northern Jiangsu Province Hospital, Yangzhou, China, 2Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
This
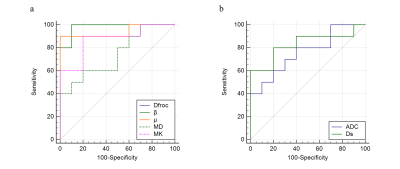
study evaluated the performance of FROC, DK, bi- and mono-exponential diffusion
models in differentiating low- from high-grade ccRCCs. As a result, the
diffusion parameters from the FROC model outperformed the other three models in
characterizing ccRCC grades.
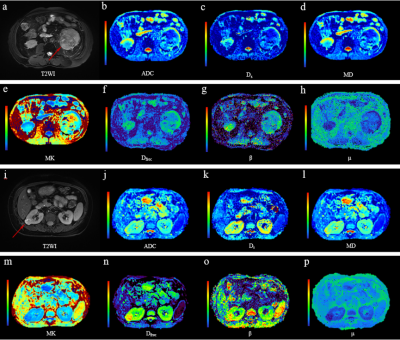
Fig.
1: (a-h) A 59-year-old man with a high-grade ccRCC (WHO grade IV) in the left
kidney. The lesion (red arrow) showed moderate signal intensity on T2-weighted
image (a), (b-h) corresponding parametric maps (ADC, Ds, MD, MK, Dfroc,
β and μ). (i-p) A 49-year-old woman with a low-grade ccRCC (WHO grade I) in the
right kidney. The lesion (red arrow) showed high signal intensity on
T2-weighted image (i), (j-p) corresponding parametric maps (ADC, Ds, MD, MK,
Dfroc, β and μ).