Alicia Cronin1,2, Patrick Liebig3, Sarah Detombe4, Neil Duggal4, and Robert Bartha1,2
1Medical Biophysics, University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2Centre for Functional and Metabolic Mapping, Robarts Research Institute, London, ON, Canada, 3Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany, 4Clinical Neurological Sciences, University Hospital, London Health Sciences Centre, London, ON, Canada
1Medical Biophysics, University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2Centre for Functional and Metabolic Mapping, Robarts Research Institute, London, ON, Canada, 3Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany, 4Clinical Neurological Sciences, University Hospital, London Health Sciences Centre, London, ON, Canada
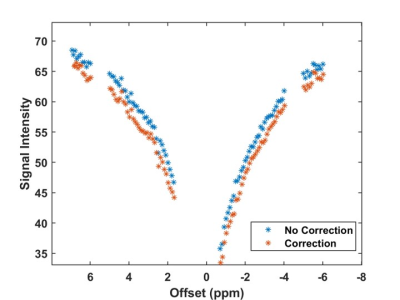
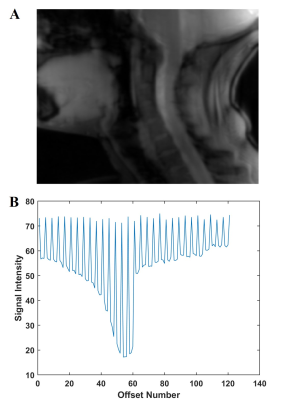
A prototype 2D gradient echo CEST
sequence utilizing a gradient-echo readout with centric reordering on a
Siemens scanner was utilized in conjunction with a respiratory correction
method to improve amide proton CEST contrast at 3.0 T in the spinal cord.