Eun-Jung Choi1, Koung Mi Kang2, Woojin Jung1, Jongho Lee1, Seung Hong Choi2, and Yong Hwy Kim3
1Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
1Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
DTI and NODDI parameters
in the optic radiations were significantly correlated with a preoperative
visual field impairment score and associated with improvement of postoperative
visual field impairment in patients with the compression of optic chiasm.
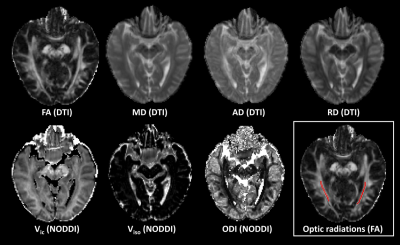
Figure 1. Representative DTI and NODDI parameter maps. The each side optic radiation
was drawn on the FA map.
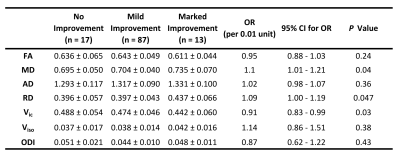
Figure 4. DTI
and NODDI Parameters and Postoperative Visual Field Improvement. Ordinal
logistic regression was performed using 3 ordinal outcomes (no improvement or
worse after surgery, Δ VFIS = 0 ~ 4; mild improvement after surgery, Δ VFIS =
-4 ~ -1; and marked improvement after surgery, Δ VFIS = -8 ~ -5).