Jan Martin1, Patrik Brynolfsson2,3, Michael Uder4, Frederik Bernd Laun4, Daniel Topgaard1, and Alexis Reymbaut2
1Physical Chemistry, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2Random Walk Imaging AB, Lund, Sweden, 3NONPI Medical AB, Umeå, Sweden, 4Institute of Radiology, University Hospital Erlangen, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), Erlangen, Germany
1Physical Chemistry, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2Random Walk Imaging AB, Lund, Sweden, 3NONPI Medical AB, Umeå, Sweden, 4Institute of Radiology, University Hospital Erlangen, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), Erlangen, Germany
Diffusion tensor distribution imaging (DTD) is a versatile inversion technique for tensor-valued diffusion data that suffers from a high noise-sensitivity (significant estimation biases). We show in silico that denoising of the data prior to analysis drastically improves DTD's accuracy.
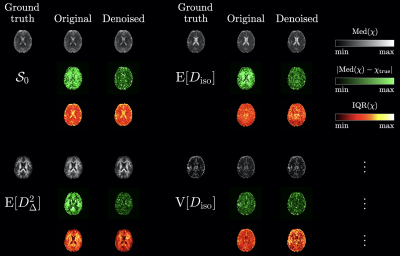
Fig.4: Typical axial maps of the ground-truth statistical descriptors of interest, $$$\chi=\mathcal{S}_0,\mathrm{E}[D_\mathrm{iso}],\mathrm{E}[D_\Delta^2],\mathrm{V}[D_\mathrm{iso}]$$$, along with the corresponding median (greyscale), bias (black-to-green) and uncertainty (black-to-red-to-yellow) parameter maps estimated across noise realizations in the original and denoised datasets. For a given statistical descriptors, all maps of a given colormap type share identically bounded color bar limits, for comparison.
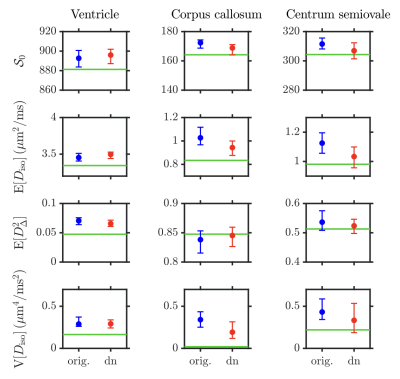
Fig.3: Histograms showing the median and interquartile range of the following DTD statistical descriptors estimated in the voxels of interest of Fig.2 in the "original" and "denoised" (dn) datasets: $$$\mathcal{S}_0$$$, mean diffusivity $$$\mathrm{E}[D_\mathrm{iso}]$$$, squared normalized anisotropy $$$\mathrm{E}[D_\Delta^2]$$$, and the variance of isotropic diffusivities $$$\mathrm{V}[D_\mathrm{iso}]$$$. While $$$D_\mathrm{iso}$$$ denotes the isotropic diffusivity, $$$D_\Delta$$$ is the normalized anisotropy.26 Green lines: ground-truth values.