Joshua Michael McAteer1, Olivier Mougin1, James Harkin2, Paul Glover1, and Penny Gowland1
1Physics, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom, 2Medicine, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom
1Physics, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom, 2Medicine, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom
Optimising compressed sensing sampling can yield a significant increase in measured and observed image quality over heuristic sampling methods. Using an example image, such as a previous acquired scan of the same anatomy, a sampling pattern can be designed that optimally samples the data.
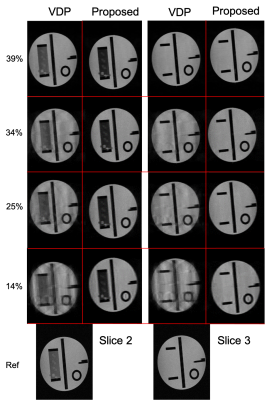
Figure 2. Example images from the reconstructions. The columns show the results of different sampling masks VPD or the proposed optimised method. The rows show different sampling density. The left block shows slice 2 of the data set, and the right block slice 3 of the data set. The fully sampled slices are shown at the bottom.
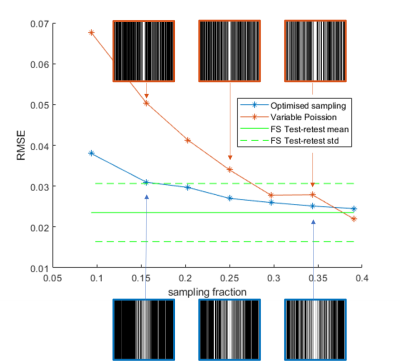
Figure 4. Image quality metric score as a function of density for the RMSE image quality metric, closer to zero is better. The VDP and optimised sampling patterns for 14%, 25%, and 34% are show for both sampling methods. The fully sampled test-retest level is shown in green. In most cases the optimised sampling gives better scores than the VDP.
