Jack R. Warren1, Matthew J. Middione2, Julio A. Oscanoa2,3, Christopher M. Sandino4, Shreyas S. Vasanawala2, and Daniel B. Ennis2,5
1Department of Computing + Mathematical Sciences, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 4Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 5Cardiovascular Institute, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
1Department of Computing + Mathematical Sciences, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 4Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 5Cardiovascular Institute, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
A previously described DL-ESPIRiT
network for the reconstruction of highly accelerated 2D Phase Contrast MRI data
was evaluated using k-fold cross validation to aid in the understanding
of the accuracy and precision of clinically relevant measures of flow.
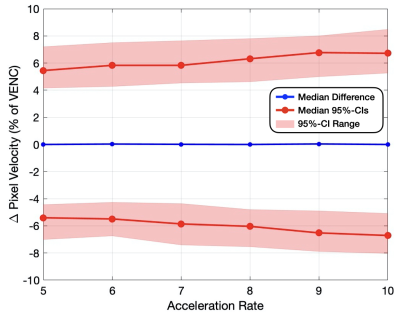
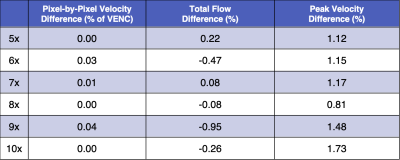
Figure 1: Vessel ROI pixel-by-pixel velocity
difference compared to FS (% of VENC) measured in percent error for acceleration rates 5-10x.
The maximum, minimum, and medians (variance) for both the upper and lower
bounds on the 95% confidence intervals are displayed for each acceleration rate
(red), as well as the median flow difference (bias) for the 8 folds (blue).