Haikun Qi1, Gastao Cruz1, Thomas Kuestner1, Karl Kunze2, Radhouene Neji2, René Botnar1, and Claudia Prieto1
1School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 2MR Research Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Limited, Frimley, United Kingdom
1School of Biomedical Engineering and Imaging Sciences, King's College London, London, United Kingdom, 2MR Research Collaborations, Siemens Healthcare Limited, Frimley, United Kingdom
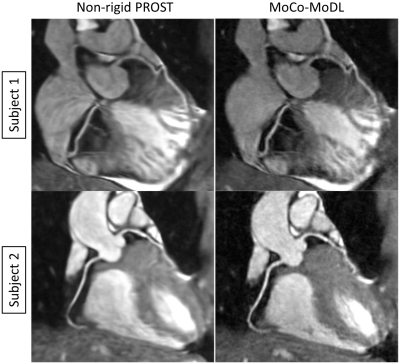
In this study, we propose an end-to-end deep learning non-rigid motion-corrected reconstruction technique for fast reconstruction of highly undersampled free-breathing CMRA.