Mohamad Abdi1, Daniel S Weller1,2, and Frederick H Epstein1,3
1Biomedical Engineering, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, United States, 2Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, United States, 3Radiology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, United States
1Biomedical Engineering, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, United States, 2Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, United States, 3Radiology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, United States
We introduce a new motion model for displacement
encoding with stimulated echoes imaging and a strategy for motion compensation in
segmented acquisitions. A Deep learning method is developed and shown to be an effective solution to estimate
the required parameters for motion compensation.
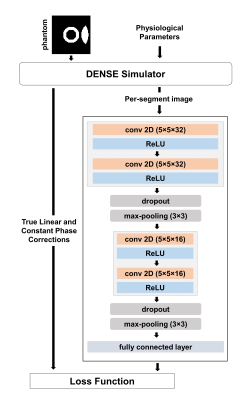
Diagram of an encoder-type
convolutional neural network to estimate linear and constant phase corrections
for motion-corrupted DENSE and it’s training using data generated with the
DENSE simulator.
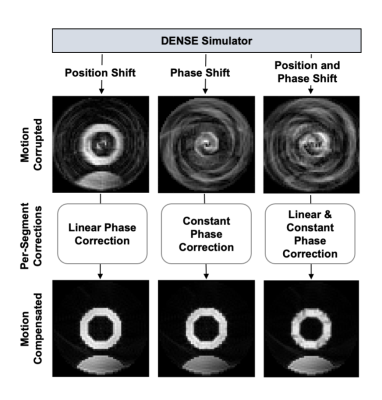
Bloch-equation-based
simulations show the various effects of free breathing during the acquisition
of DENSE images (top row of images). Motion-compensation based on Equation 4
demonstrates the validity of the motion model and its ability to achieve motion
correction if the phase correction values are known (bottom row of images).