Christopher Sica1, Hairong Chen2, Guangwei Du2, Sangam Kanekar1, Jianli Wang1, Qing X Yang3, and Prasanna Karunanayaka1
1Radiology, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States, 2Neurology, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States, 3Neurosurgery, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States
1Radiology, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States, 2Neurology, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States, 3Neurosurgery, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States
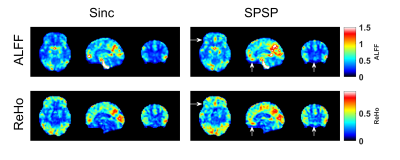
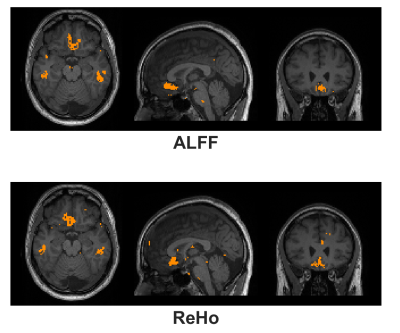
fMRI scans with long echo
times are vulnerable to signal loss due to through-plane dephasing caused by
susceptibility field gradients. This work evaluates the ability of phase-precompensated spectral-spatial RF pulses to improve detection of resting state fMRI activity in these regions.