Wei Zhao1, Huanjie Li1, Yunge Zhang1, Blaise B. Frederick 2, and Fengyu Cong1
1Biomedical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2Department of Psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
1Biomedical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2Department of Psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
Proposed adapted NPE algorithm is an efficient dimensionality reduction method that has better performance on individual and group level analysis using
fMRI data applied with Independent Component Analysis, as well as improvements on the reliability and reproducibility.
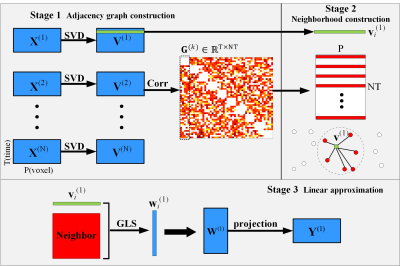
Fig. 1. Three stages of adapted NPE for fMRI. (1): The N subjects are applied with SVD and the correlation are used to form the adjacency graph. The green strip denotes a spatial eigenvector from sub#1. Each dot denotes a connection, and the darker colors denotes stronger connection. (2): The red strips and dots are qualified components forming a neighborhood with green one, while white dots are disqualified components with weak connection. (3): The Linear approximation is employed to compute the weight with well-constructed neighborhood and followed with projection to obtain results.
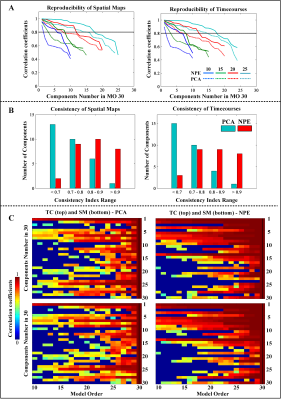
Fig. 4. The consistency analyses for spatial-temporal ICs of Group ICA under model order 30. (A) The lines are the sorted correlation of paired ICs in lower MO, 10(blue), 15 (green), 20 (red), and 25 (light blue) with IC in MO 30. The horizonal black dotted line is set as 0.8 to quantify reproducible ICs from NPE (solid line) and PCA (dotted line). (B) The bar height denotes IC numbers in different consistency index ranges (<0.7, 0.7-0.8, 0.8-0.9, >0.9) for NPE (red) than PCA (light blue). (C) Correlation maps of paired ICs from MO 10 to 30 with ICs in MO 30.