Xiao Wu1, Yue Zhang2, and Ji-lei Zhang3
1Department of chinese medicine, Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
1Department of chinese medicine, Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
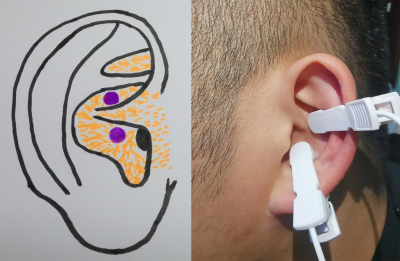
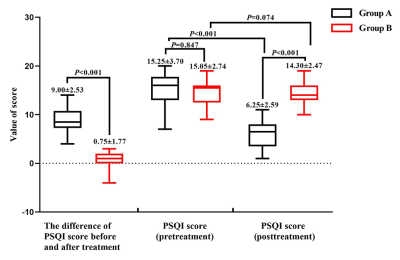
Our study aimed at comparing the differences of fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (fALFF) value and heart rate variability (HRV) between “effective group (group A)” and “non-effective group (group B)” during continuous taVNS to analyze the neuro-brain functional mechanisms that caused the different efficacy of taVNS to primary insomnia (PI), so as to provide clinical and theoretical basis for individualized treatment of taVNS. We got these conclusions that the regulation of SMN to HRV during continuous taVNS are may the mechanism that caused the different efficacy of taVNS. The HRV indicators and fALFF value of SMN during the continuous taVNS were might the bio-markers that could predict the efficacy of taVNS on insomnia.