Yiming Wang1, Limin Zhou1, Durga Udayakumar1,2, and Ananth J. Madhuranthakam1,2
1Radiology, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States, 2Advanced Imaging Research Center, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States
1Radiology, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States, 2Advanced Imaging Research Center, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States
We assessed
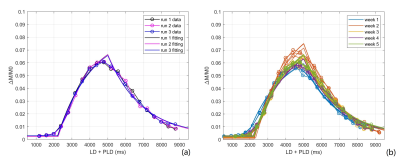
the reproducibility and repeatability of perfusion measurements using multi-PLD
2D pCASL over 5 weeks with a 3D-printed perfusion phantom. Intra-class
correlation coefficients of measured perfusion and T1 are 0.96 and 0.94,
indicating good reproducibility and repeatability.