Rebeca Echeverria-Chasco1,2, Marta Vidorreta3, Veronica Aramendia-Vidaurreta2,4, David Cano 1, Gorka Bastarrika2,4, Nuria Garcia-Fernandez2,5, Paloma L. Martin Moreno2,5, and Maria A. Fernandez-Seara2,4
1Radiology, Clínica Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, NE, Spain, 2IdiSNA, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain, 3Siemens Healthineers, Madrid, Spain, 4Radiology, Clínica Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain, 5Nephrology, Clínica Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain
1Radiology, Clínica Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, NE, Spain, 2IdiSNA, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain, 3Siemens Healthineers, Madrid, Spain, 4Radiology, Clínica Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain, 5Nephrology, Clínica Universidad de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain
Reproducibility of multiparametric MRI (perfusion, diffusion and T1 mapping) was assessed in renal allograft
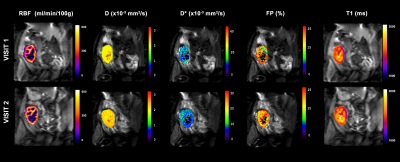
Figure 1: Example of multiparametric MRI maps acquired during
the two MRI exams: arterial spin labeling perfusion maps, diffusion coefficient
(D) maps, pseudo-diffusion coefficient (D*) maps, perfusion fraction maps
and longitudinal relaxation (T1) maps.
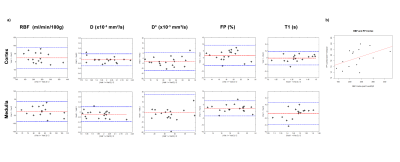
Figure 2: a) Bland-Almant plots for the RBF (ml/min/100g), D (×10−3 mm2/s), D* (×10−3 mm2/s), PF (%) and T1 (ms) calculated in the cortex and in the medulla. b) Correlation between cortical mean values of renal blood flow and perfusion fraction averaged for the two exams, with a correlation coefficient r = 0.47.
