Lucas Soustelle1,2, Andreea Hertanu1,2, Arnaud Le Troter1,2, Soraya Gherib1,2, Samira Mchinda1,2, Patrick Viout1,2, Lauriane Pini1,2, Claire Costes1,2, Sylviane Confort-Gouny1,2, Adil Maarouf1,2,3, Bertrand Audoin1,2,3, Audrey Rico1,2,3, Clémence Boutière1,2,3, Maxime Guye1,2, Jean-Philippe Ranjeva1,2, Gopal Varma4, David C. Alsop4, Jean Pelletier1,2,3, Guillaume Duhamel1,2, and Olivier M. Girard1,2
1Aix Marseille Univ, CNRS, CRMBM, Marseille, France, 2APHM, Hôpital Universitaire Timone, CEMEREM, Marseille, France, 3APHM, Hôpital Universitaire Timone, Service de neurologie, Marseille, France, 4Division of MR Research, Radiology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
1Aix Marseille Univ, CNRS, CRMBM, Marseille, France, 2APHM, Hôpital Universitaire Timone, CEMEREM, Marseille, France, 3APHM, Hôpital Universitaire Timone, Service de neurologie, Marseille, France, 4Division of MR Research, Radiology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
Characterization
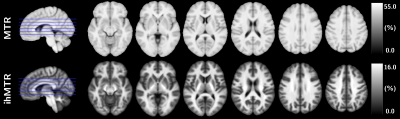
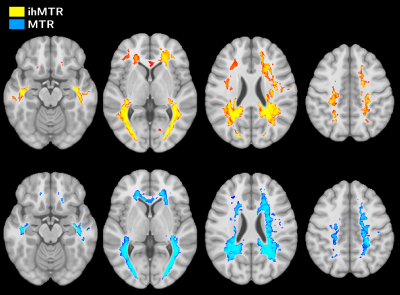
of WM impairments in MS is performed by comparing ihMT and conventional MT normalized
in a standard space. Results revealed how the signal in normal-appearing and
lesional WM is affected, and highlighted that both metrics provide
complementary information.