Poljanka Johnson1, Irene M Vavasour2, Shawna Abel1, Lisa E Lee3, Stephen Ristow1, Cornelia Laule4, Roger Tam2, David K.B. Li2, Nathalie Ackermans1, Alice Schabas1, Jillian Chan1, Helen Cross1, Ana-Luiza Sayao1, Virginia Devonshire1, Robert Carruthers1, Anthony Traboulsee3, and Shannon Kolind5
1Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2Radiology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4Radiology, Physics and Astronomy, Pathology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 5Medicine, Physics & Astronomy, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
1Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2Radiology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4Radiology, Physics and Astronomy, Pathology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 5Medicine, Physics & Astronomy, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
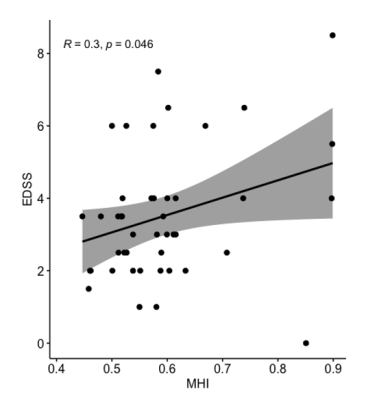
This study investigates a potential myelin related metric for discriminating between MS subtypes. This study also demonstrates that normal appearing white matter in MS shows increased myelin damage in individuals with worse disability.
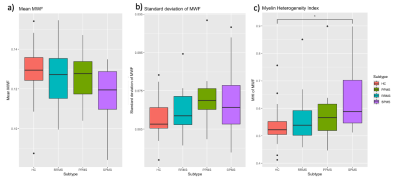
The myelin water fraction (MWF) a) mean, b) standard deviation, and c) coefficient of variation (or myelin heterogeneity index, MHI) of the normal appearing white matter in healthy controls (HC), relapsing remitting MS (RRMS), primary progressive MS (PPMS), and secondary progressive MS (SPMS). A one-way ANOVA test with Tukey correction showed that the MHI of SPMS was higher than HC (p=0.01) and trended towards higher than RRMS (p=0.065).