Stefania Oliviero1 and Cosimo Del Gratta1
1Department of Neuroscience, Imaging, and Clinical Sciences, University of Chieti Pescara G. D'Annunzio, Chieti, Italy
1Department of Neuroscience, Imaging, and Clinical Sciences, University of Chieti Pescara G. D'Annunzio, Chieti, Italy
DKI
metrics significantly changed with axonal loss but not with demyelination,
while NODDI metrics showed sensitivity to both damage processes. In any case, the
sequence strongly affected the sensitivity and, especially for NODDI, the
metric means.
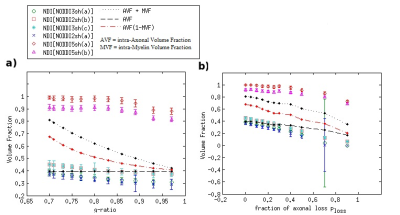
Fig 2 Results for the Neurite Density Index NDI (i.e. the NODDI-derived intra-cellular
fractional volume), using 6 different
acquisition protocols. In a and b, NDI mean values and standard deviations obtained
in different conditions of demyelination and axonal loss, respectively, considering a Rician
noise with SNR=20 affects the synthetic DW signal. For reference, some
specific combinations of the true intra-axonal volume fraction AVF and true
intra-myelin volume fraction MVF are also shown.
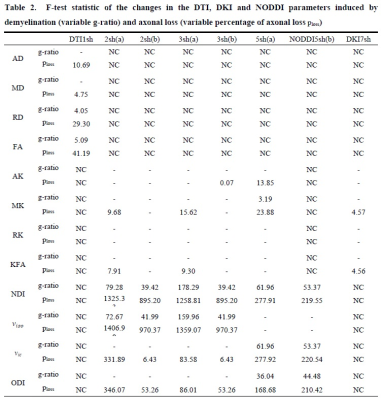
Metrics AD, MD, RD, and FA are DTI-derived; AK,
MK, RK, and KFA are DKI-derived, while neurite density index NDI, fractional
volume
of the isotropic compartment νiso,
fractional volume νic of the intra-cellular
space, and orientation
dispersion index ODI are NODDI-derived. Omitted results (-)
refer to parameters showing non-significant changes between healthy and damaged
condition (one-way ANOVA with p<0.01). NC means Not Calculated, since not all the sequences were used for all
the DWI analyses.
