Francisca F. Fernandes1, Rita Gil1, Jonas L. Olesen2,3, Sune N. Jespersen2,3, and Noam Shemesh1
1Champalimaud Research, Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, Lisbon, Portugal, 2Center of Functionally Integrative Neuroscience (CFIN) and MINDLab, Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, 3Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark
1Champalimaud Research, Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, Lisbon, Portugal, 2Center of Functionally Integrative Neuroscience (CFIN) and MINDLab, Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, 3Department of Physics and Astronomy, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark
MP-PCA denoising increased the sensitivity of fMRI towards BOLD signal changes in response to visual stimulation in the mouse as well as the tSNR of the measurements, thereby improving the capacity of BOLD fMRI to image brain activity.
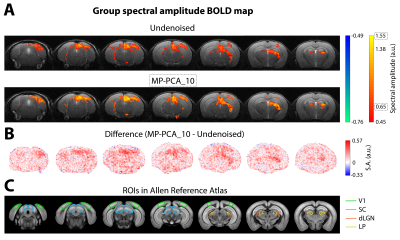
Fig. 3 – Group conventional fMRI results (n=3). (A) Group BOLD Fourier maps computed from data of 9 individual scans without denoising (top) and after MP-PCA_10 denoising (bottom). (B) Difference of spectral amplitude maps at the fundamental frequency between MP-PCA_10 and undenoised data. (C) Regions of interest (ROIs) of the mouse visual pathway delineated on the Allen Reference Atlas.
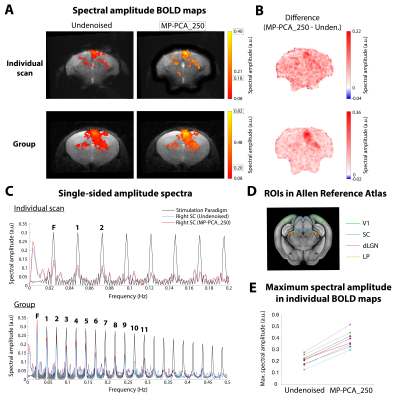
Fig. 4 – Ultrafast fMRI results. (A) Individual (top) and group (bottom, n=3, 9 scans) BOLD Fourier maps from ultrafast data, before and after MP-PCA_250 denoising. (B) Difference between spectral maps. (C) Amplitude spectra from the stimulation paradigm and from the right SC’s signal, using undenoised and MP-PCA_250 data from an individual scan (top) or all scans (bottom). (D) ROIs in the oblique brain slice. (E) Variation of maximum spectral amplitude in 9 individual maps with denoising.
