Lenka Dvořáková1, Petteri Stenroos1, Ekaterina Zhurakovskaya1, Raimo Salo1, Jaakko Paasonen1, and Olli Gröhn1
1A.I.V. Institute for Molecular Sciences, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland
1A.I.V. Institute for Molecular Sciences, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland
The aim of this study was to investigate a light sedation pre-clinical fMRI protocol with a
short habituation period. We found that apart from slightly modified thalamic
connectivity light sedation provides results comparable to the data obtained in the awake state.
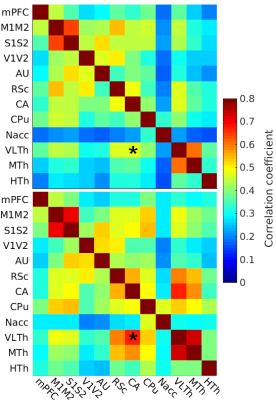
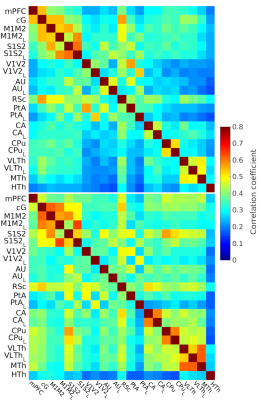
Fig 1: The
FC of light sedated animals (top, N = 102) and awake (bottom, N = 10) were
compared with the FDR-corrected studentized permutation test, *p<0.05; medial
prefrontal cortex (mPFC), motor cortex (M1M2), somatosensory cortex (S1S2), visual
cortex (V1V2), auditory cortex (AU), retrosplenial cortex (RSc), hippocampus (CA),
striatum (CPu), nucleus accumbens (Nacc), ventrolateral thalamus (VLTh), medial
thalamus (MTh), hypothalamus (HTh).