Zengmin Li1, Dilsher Athwal1, and Kai-Hsiang Chuang1,2
1Queensland Brain Institute, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Australia, 2Centre for Advance Imaging, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
1Queensland Brain Institute, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Australia, 2Centre for Advance Imaging, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
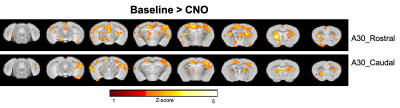
To understand role of DMN in memory consolidation, we inhibit the retrosplenial cortex, area 30 (A30) after mice learned a spatial memory task and we found connectivity reduction correlated with behavior performance.
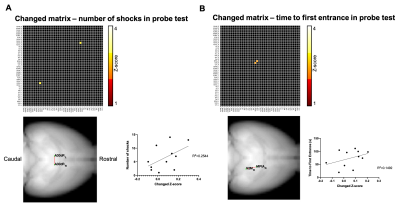
Fig.3 Two examples of the correlation between connectivity and behavior indices. (A,B) The upper matrix shows the functional connection which significantly correlated with either number of shocks or time to the first entrance in the probe test. p<0.01, uncorrected. The lower left shows the anatomical location of the connection. The lower right shows the scatter plot between connectivity change (Z-score) and behavior indices.