Shufang Wei1, Jiajia Li1, Xianchang Zhang2, Jing An3, and Yinghui Ge1
1Fuwai Central China Cardiovascular Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China, 3Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Shenzhen, China
1Fuwai Central China Cardiovascular Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd, Beijing, China, 3Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Shenzhen, China
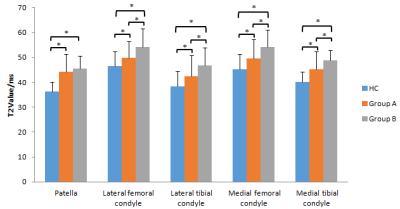
T2 mapping detected early cartilage changes in patients with hemophilia and could be used as a sensitive biomarker to detect these early changes and develop preventative treatment plans.
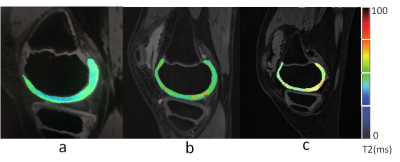
T2 mapping (T2M) of the knee. (a) Control group, male, 10 yo; T2M pseudo-color imaging (PCI) shows a uniform cartilage color distribution and complete articular surface. (b) Group A, male, 9 yo; T2M PCI shows uneven cartilage color distribution, few red-yellow stage changes, and an increased cartilage T2 value. (c) Group B, male, 11 yo; T2M PCI shows greater uneven cartilage color distribution, a significantly diminished weight-bearing area, and a significantly increased cartilage T2 value.