Hyungseok Jang1, Yajun Ma1, Michael Carl2, Saeed Jerban1, Eric Y Chang1,3, and Jiang Du1
1University of California, San Diego, San Diego, CA, United States, 2GE Healthcare, San Diego, CA, United States, 3Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System, San Diego, CA, United States
1University of California, San Diego, San Diego, CA, United States, 2GE Healthcare, San Diego, CA, United States, 3Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System, San Diego, CA, United States
The proposed single-point
Dixon (spDixon)-based fat suppression achieved high contrast Ultrashort Echo
Time Double Echo Steady State (UTE-DESS) imaging of short T2 tissues. We demonstrated
that fat suppression with spDixon technique improved lesion detection in human knee
joints.
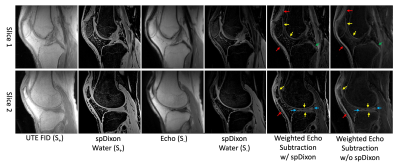
Figure 4.
UTE-DESS imaging with spDixon of knee joint of a healthy volunteer
(37-year-old male). Both weighted echo subtractions with and without spDixon-based fat
suppression achieve high contrast specific to short T2 tissues
including the osteochondral junction (yellow arrows), tendons (red arrows),
menisci (blue arrows), and ligaments (green arrows).
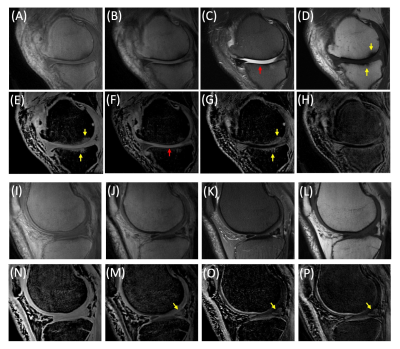
Figure 5.
UTE-DESS imaging with spDixon in two representative OA patients (A-H: 52-year-old
male, I-P: 56-year-old male). (A, I) Magnitude images of S+, (B, J)
magnitude images of S-, (C, K) T2-FSE images, (D, L) T1-FSE
images, (E, N) spDixon water images from S+, (F, M) spDixon water images from S-,
(G, O) weighted echo subtraction of water images from spDixon, and (H, P)
weighted echo subtraction of S+ and S- without spDixon.