1Radiology, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan, 2Joint Research Laboratory of Advanced Medical Imaging, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan, 3Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan, 4Radiology, Fujita Health University Hospital, Toyoake, Japan

Figure 1. 71-year old patient with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. (First line from L to R: MRCPFAST 3D with AiCE, MRCPCompressed SPEEDER with AiCE and MRCPconventional SPEEDER with AiCE; second line from L to R: MRCPFAST 3D without AiCE, MRCPCompressed SPEEDER without AiCE and MRCPconventional SPEEDER without AiCE).
MRCPFAST 3D and MRCPconventional SPEEDER more clearly depict intrahepatic bile duct as well as main pancreatic duct than MRCPCompressed SPEEDER, when applied AiCE or not. In addition, AiCE was able to improve image quality of MRCP obtained by each technique.
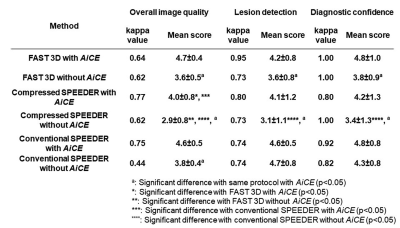
Figure 4. Compared results of interobserver agreement and qualitative image qualities among all methods.
Interobserver agreement on each method was ranged between 0.44 and 0.77. When applied AiCE, each index on MRCP obtained by each technique and reconstructed with AiCE were significantly higher than those without AiCE (p<0.05). On each index, MRCPCompressed SPEEDER with and without AiCE were significantly lower than MRCPFAST 3D or MRCPconventional SPEEDER with and without AiCE (p<0.05).
