Junyu Guo1 and Ivan Pedrosa1
1Radiology, UT southwestern medical center, Dallas, TX, United States
1Radiology, UT southwestern medical center, Dallas, TX, United States
In this study, we investigated the feasibility of kidney segmentation using deep learning models trained with MR images from only a few subjects. We tested the hypothesis that few-shot deep learning may achieve accurate kidney segmentation.
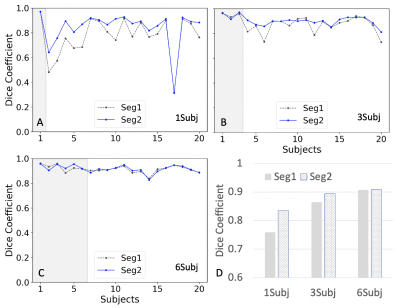
Figure 2. Comparison between two results (Seg1 vs. Seg2) of Dice coefficients using the different trained models. A.) Dice coefficient plots from a model trained using one subject (1Subj); B.) using three subjects (3Subj); C.) using the six subjects (6Subj). D.) the bar plots for the above three cases. Seg1 indicates the results predicted using the first network alone; Seg2 indicates the results by using the two networks in Fig. 1. Gray areas in A-C indicate the training data sets.
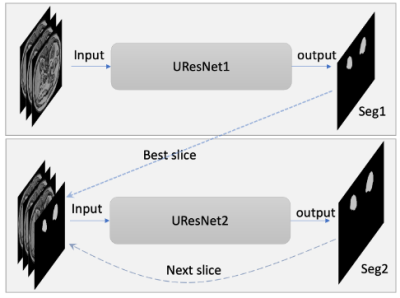
Figure 1. Diagram of two neural networks including UResNet1 and UResnet2. The inputs for UResNet1 are three consecutive slices; the inputs for UResNet2 are three consecutive slices and one predicted mask for the third slice. Seg1 indicates the output of the first network; Seg2 indicates the output of the whole networks. The dotted and dashed lines indicate the relationship in the prediction stage.
