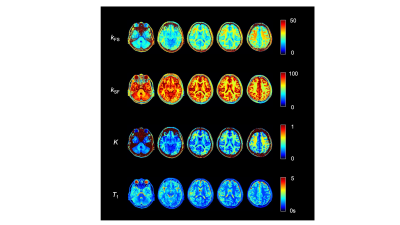
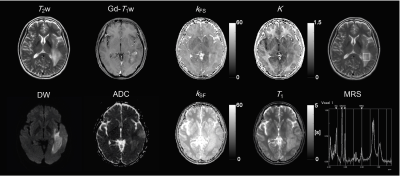
Naoki Maeda1, Yuki Kanazawa2, Masafumi Harada2, Yo Taniguchi3, Yuki Matsumoto2, Hiroaki Hayashi4, Kosuke Ito3, Yoshitaka Bito3, and Akihiro Haga2
1Graduate of Health Science, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan, 2Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan, 3Healthcare Business Unit, Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, 4College of Medical, Pharmaceutical and Health Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan
1Graduate of Health Science, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan, 2Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan, 3Healthcare Business Unit, Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, 4College of Medical, Pharmaceutical and Health Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan
For brain structures in healthy subjects, there was a significant negative correlation between water exchange rates. Some interesting findings were observed in abnormal tissue. Our method using QPM enabled to evaluate water proton diffusion between structures based on cross-relaxation.