Zhitao Li1,2, Zhiyang Fu3, and Maria I Altbach4
1Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, United States, 2Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, United States, 3Electrical and Computer Engineering, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States, 4Department of Medical Imaging, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States
1Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, United States, 2Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, United States, 3Electrical and Computer Engineering, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States, 4Department of Medical Imaging, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States
A 3D IR-radFLASH pulse sequence and a corresponding model-based reconstruction algorithm is presented for in vivo brain T1 mapping with high spatiotemporal resolution and high SNR. The proposed sequence can achieve whole brain coverage under 5 minutes.
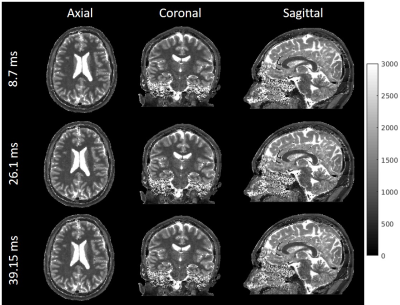
Figure 4. Reconstructed brain T1 maps from data acquired with 3D IR-radFLASH technique at 1.0 mm isotropic resolution. Data were reconstructed with the algorithm shown in Figure 1b at temporal resolutions of 8.7ms, 26.1ms and 39.15ms. The 1.00 mm isotropic T1 maps are presented in axial, coronal and sagittal orientations. The high resolution preserves the brain anatomical details in the T1 map. Whole brain data were acquired under 5 minutes.
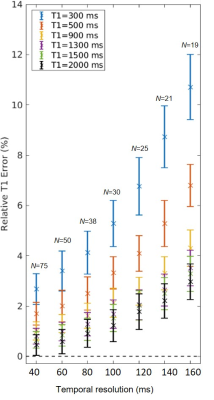
Figure 2. Computer simulations of the effect of the temporal resolution on T1 error for a range of T1 values. The simulations were based on sampling the recovery curve over 3 seconds, thus for each temporal resolution a different number of TI points (indicated by N in the plot) was used to fit the data. Data were simulated by adding noise corresponding to 32dB and using 100 noise realizations.