Xinlin Zhang1, Hengfa Lu2, Zi Wang1, Xi Peng3, Feng Huang4, Qin Xu4, Di Guo5, and Xiaobo Qu1
1Department of Electronic Science, School of Electronic Science and Engineering (National Model Microelectronics College), National Institute for Data Science in Health and Medicine, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 2College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 3Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States, 4Neusoft Medical System, Shanghai, China, 5School of Computer and Information Engineering, Fujian Provincial University Key Laboratory of Internet of Things Application Technology, Xiamen University of Technology, Xiamen, China
1Department of Electronic Science, School of Electronic Science and Engineering (National Model Microelectronics College), National Institute for Data Science in Health and Medicine, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 2College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 3Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States, 4Neusoft Medical System, Shanghai, China, 5School of Computer and Information Engineering, Fujian Provincial University Key Laboratory of Internet of Things Application Technology, Xiamen University of Technology, Xiamen, China
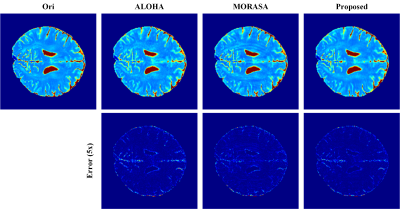
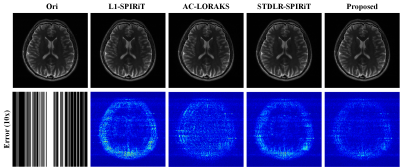
This work proposed a new strategy for enforcing the low-rankness of Hankel
matrix of MRI data to not only provide reconstruction results with lower errors
but achieve lower computation and memory. The advantages
of the proposed method are validated in both 2D imaging and T2 mapping scenarios.