Jianbao Wang1,2, Shahin Nasr2,3, Anna Wang Roe1,4, and Jonathan R. Polimeni2,3,5
1Department of Neurology of the Second Affiliated Hospital, Interdisciplinary Institute of Neuroscience and Technology, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 3Department of Radiology, Harvard Medical School, Charlestown, MA, United States, 4Key Laboratory for Biomedical Engineering, of Ministry of Education, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 5Division of Health Sciences and Technology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, United States
1Department of Neurology of the Second Affiliated Hospital, Interdisciplinary Institute of Neuroscience and Technology, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 3Department of Radiology, Harvard Medical School, Charlestown, MA, United States, 4Key Laboratory for Biomedical Engineering, of Ministry of Education, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 5Division of Health Sciences and Technology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, United States
We
suggest several approaches to reduce losses in spatial accuracy in high-resolution
fMRI imposed during data acquisition and processing and recommend methods for
quantifying the spatially-varying resolution. These methods can provide spatial
“error bars” to use when evaluating results.
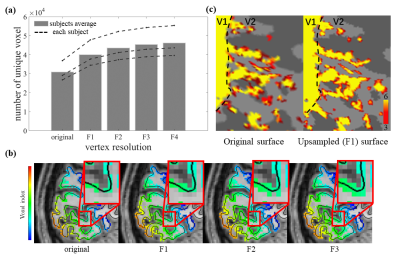
Fig.
4: Effect of surface mesh upsampling on representing fine-scale features. (a) The
number of unique fMRI voxel for different surface upsampling factors ranging from
1 to 4, and for the original surface. Dashed lines represent these values for each
individual subject; bars show the average across subjects. (b) Voxels missing
from when using the original surface that were captured with increasing upsampling
factors. Color indicates voxel index. (c) Thin-stripe columnar pattern detected
in V2 from original surface and upsampled surface. p<0.001. Value of color
bar: −log(p).
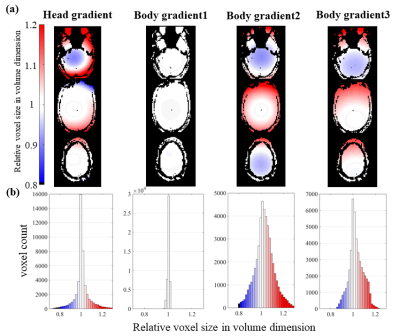
Fig.
5: Spatial nonuniformity of resolution induced by geometric distortion, in this
case due to gradient nonlinearity. Voxel size varies smoothly across brain
regions due to geometric expansion and compression from gradient nonlinearity,
which varies with the design of the gradient coil. Examples from whole-brain
axial slices (a) and histogram (b) show the spatial distribution of relative
voxel size in volume dimension. Color gradient from blue to red indicate
smaller to larger true voxel sizes.