Xiangrui Li1, Oyetunde Gbadeyan 1, and Ruchika Shaurya Prakash1
1Department of Psychology and Center for Cognitive and Behavioral Brain Imaging, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, United States
1Department of Psychology and Center for Cognitive and Behavioral Brain Imaging, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, United States
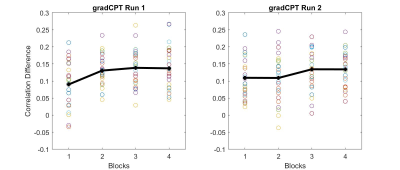
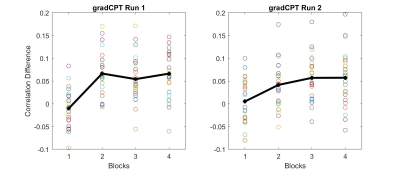
Combined connectome-based models of sustained attention and
mind-wandering are representative of high and low attentional states, thus
making them appropriate targets for real-time fMRI neurofeedback.