Xeni Deligianni1,2, Francesco Santini1,2, Matteo Paoletti3, Francesca Solazzo3, Niels Bergsland4,5, Giovanni Savini3, Arianna Faggioli3, Giancarlo Germani3, Mauro Monforte6, Giorgio Tasca6, Enzo Ricci6, and Anna Pichiecchio3,7
1Department of Radiology/ Division of Radiological Physics, University Hospital of Basel, Basel, Switzerland, 2Biomedical Engineering, University of Basel, Allschwil, Switzerland, 3Advanced Imaging and Radiomics Center, Neuroradiology Department, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy, 4Buffalo Neuroimaging Analysis Center, Department of Neurology, Buffalo Neuroimaging Analysis Center, Department of Neurology, Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Buffalo, NY, United States, 5IRCCS, Fondazione Don Carlo Gnocchi ONLUS, Milan, Italy, 6Unità Operativa Complessa di Neurologia, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, Rome, Italy, 7Department of Brain and Behavioral Sciences, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy
1Department of Radiology/ Division of Radiological Physics, University Hospital of Basel, Basel, Switzerland, 2Biomedical Engineering, University of Basel, Allschwil, Switzerland, 3Advanced Imaging and Radiomics Center, Neuroradiology Department, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy, 4Buffalo Neuroimaging Analysis Center, Department of Neurology, Buffalo Neuroimaging Analysis Center, Department of Neurology, Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Buffalo, NY, United States, 5IRCCS, Fondazione Don Carlo Gnocchi ONLUS, Milan, Italy, 6Unità Operativa Complessa di Neurologia, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, Rome, Italy, 7Department of Brain and Behavioral Sciences, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy
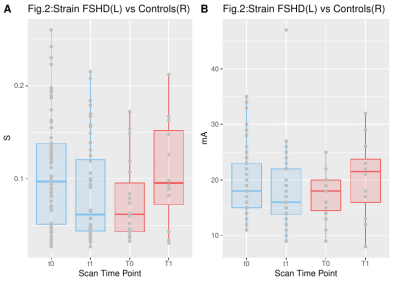
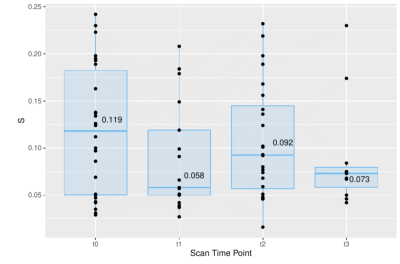
After applying MRI of muscle contraction during electrical stimulation on the quadriceps muscles longitudinally in FSHD patients and in healthy controls, differences were observed in maximum values and rates of the strain.