Yael Jacob1, Gaurav Verma1, Lara Marcuse1, Madeline Fields1, and Priti Balchandani1
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States
The ability to identify epilepsy patients (EP) early in the course of disease is greatly needed. Using multi-modal structure-function network hierarchy features as predictors in a machine learning algorithm we were able to classify EP and controls with overall accuracy of 84%.
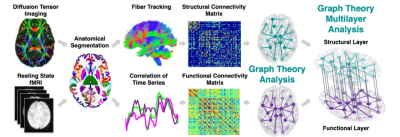
Figure 1. Connectome analysis procedure. Subject-level structural network is derived from DWI MRI data using probabilistic fiber tracking between the segmented regions of interest. Subject-level functional network is derived from resting state fMRI data based on the pairwise correlations between the regions of interest. Graph theoretical nodal centrality features are computed for both structural and functional networks and their coupling using multilayer analysis.
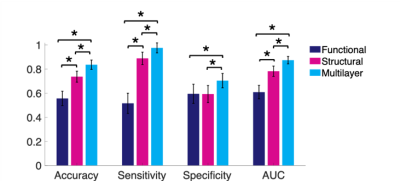
Figure 3. Classification comparison. The multi-modal multilayer based SVM classification model resulted in higher predictive values compared to classification models based on single layer of structural or functional connectomes. These results indicate the ability of the multilayer approach to provide improved classification between EP and HC. *p<0.001