Maryam Afzali1, Lars Mueller1, Ken Sakaie2, Siyuan Hu3, Yong Chen4, Mark Griswold4, Derek K Jones1, and Dan Ma3
1Cardiff University Brain Research Imaging Centre (CUBRIC), School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom, 2Imaging Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 3Biomedical Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States, 4Radiology, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States
1Cardiff University Brain Research Imaging Centre (CUBRIC), School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom, 2Imaging Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States, 3Biomedical Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States, 4Radiology, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, United States
We implement multi-dimensional MR Fingerprinting scan with linear and spherical diffusion tensor encoding to simultaneously quantify $$$T_1$$$, $$$T_2$$$ and diffusivity in a single scan .
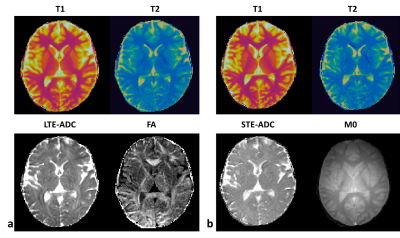
Figure 3: Estimated diffusion and relaxometry parameters. (a) $$$T_1$$$ and $$$T_2$$$ relaxation times and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and fractional anisotropy (FA) from a single slice of md-MRF scan using linear tensor encoding (LTE) (b) results of md-MRF scan using spherical tensor encoding (STE). M0 shows the proton density map.
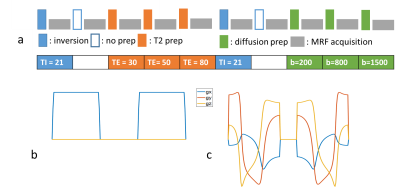
Figure 1: Sequence diagram of an acquisition unit of mdMRF scan. (a) Each acquisition unit consists of multiple inversion, $$$T_2$$$ and diffusion preparation modules with various timing and b-values. The table lists the key parameters of the modules. (b) and (c) are LTE and STE diffusion gradients used in the diffusion preparation modules.