Kevin Vallotton1, Gergely David1, Armin Curt1, Michael Fehlings2, Claudia A. M. Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott3,4,5, Rebecca S. Samson6, Julien Cohen-Adad7, Muhammad Ali Akbar2, Patrick Freund1,8,9, and Maryam Seif1
1Spinal Cord Injury Center, University Hospital Balgrist, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, Zuerich, Switzerland, 2University of Toronto Spine Program and Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3NMR Research Unit, Queen Square MS Centre, Department of Neuroinflammation, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, Faculty of Brain Sciences, University College London (UCL), London, United Kingdom, 4Department of Brain and Behavioural Sciences, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy, Pavia, Italy, 5Brain Connectivity Center Research Department, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy, 6Queen Square MS Centre, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, Faculty of Brain Sciences, London, United Kingdom, London, United Kingdom, 7Functional Neuroimaging Unit, CRIUGM, University of Montreal, Montreal, QC, Canada, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8Department of Neurophysics, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany, 9Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, UCL Institute of Neurology, London, United Kingdom
1Spinal Cord Injury Center, University Hospital Balgrist, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, Zuerich, Switzerland, 2University of Toronto Spine Program and Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3NMR Research Unit, Queen Square MS Centre, Department of Neuroinflammation, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, Faculty of Brain Sciences, University College London (UCL), London, United Kingdom, 4Department of Brain and Behavioural Sciences, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy, Pavia, Italy, 5Brain Connectivity Center Research Department, IRCCS Mondino Foundation, Pavia, Italy, 6Queen Square MS Centre, UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, Faculty of Brain Sciences, London, United Kingdom, London, United Kingdom, 7Functional Neuroimaging Unit, CRIUGM, University of Montreal, Montreal, QC, Canada, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8Department of Neurophysics, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany, 9Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging, UCL Institute of Neurology, London, United Kingdom
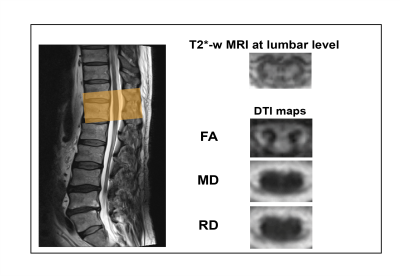
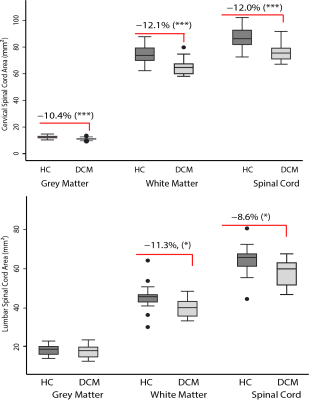
Based on T2*- and DTI-weighted MRI, similar structural changes were observed in cervical and lumbar cord of degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM) patients. The extent of cervical and lumbar cord atrophy is associated between each other in individual DCM patients.